# About Jenkins
Jenkins is an open-source automation server that automates the repetitive technical tasks involved in the continuous integration and delivery of software. Jenkins is Java-based and can be installed from Ubuntu packages or by downloading and running its web application archive (WAR) file — a collection of files that make up a complete web application to run on a server.
# How to install Jenkins on Centos 7
To install Jenkins on Centos 7, follow my bash code (or you can save it to a jenkins.sh file, then run sh jenkins.sh)
echo "Begin bash code to install Jenkins on Centos 7 server - code by Tran Viet Huy" echo "1. Jenkins is a Java application, so the first step is to install Java. Run the following command to install the OpenJDK 8 package:" sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel -y
echo "2.The next step is to enable the Jenkins repository. To do that, import the GPG key using the following curl command:"
sudo wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo sudo rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.key
#curl --silent --location http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo #sudo rpm --import https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key
echo "3.Once the repository is enabled, install the latest stable version of Jenkins by typing:"
sudo yum install jenkins -y
echo "4.After the installation process is completed, start the Jenkins service with:"
sudo systemctl start jenkins
echo "5. Check Service status again" sudo systemctl status jenkins
echo "6. Check current Firewall port, Open port 8080, then reload and check again " firewall-cmd --list-all firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload firewall-cmd --list-all
echo "More info: About the error \"Public key for jenkins-2.249.2-1.1.noarch.rpm is not installed\" Get the right public key here: https://archives.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/ "
As the bash code describe everything in detail, we can summarize them:
- Install open java
- Install jenkins
- Open port 8080
- Start jenkins service
# And the happiest moment: login to jenkins admin on port 8080
Open your web browser and fill in the address:
IP_address:8080
And now, we are at
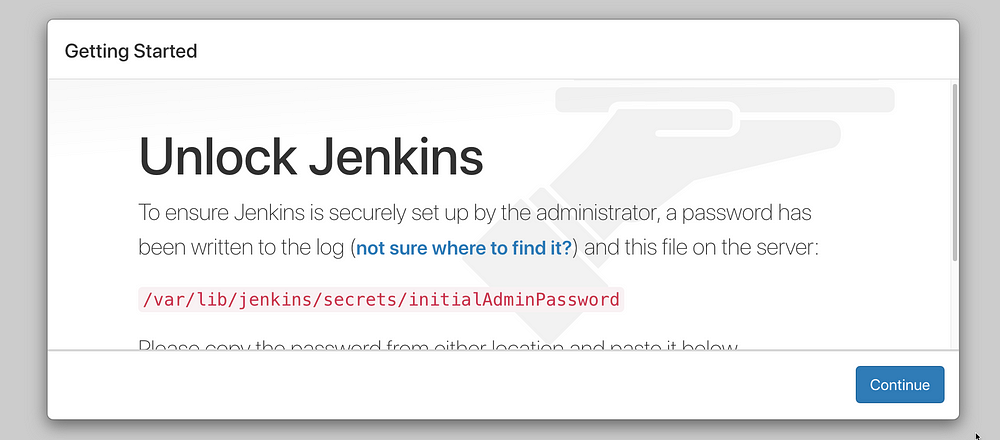
You can view Jenkins initial Admin Password with this command line
nano /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
or
vi /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Now, you have the admin password, fill in the password area and press Continue
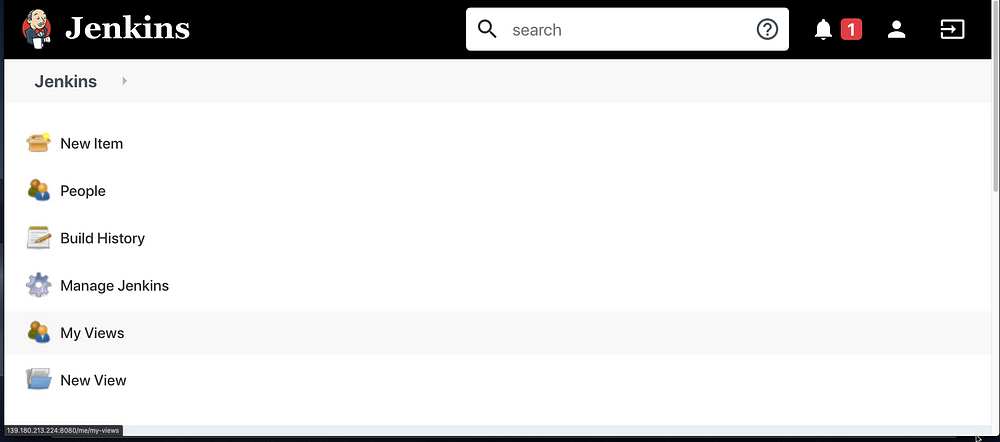
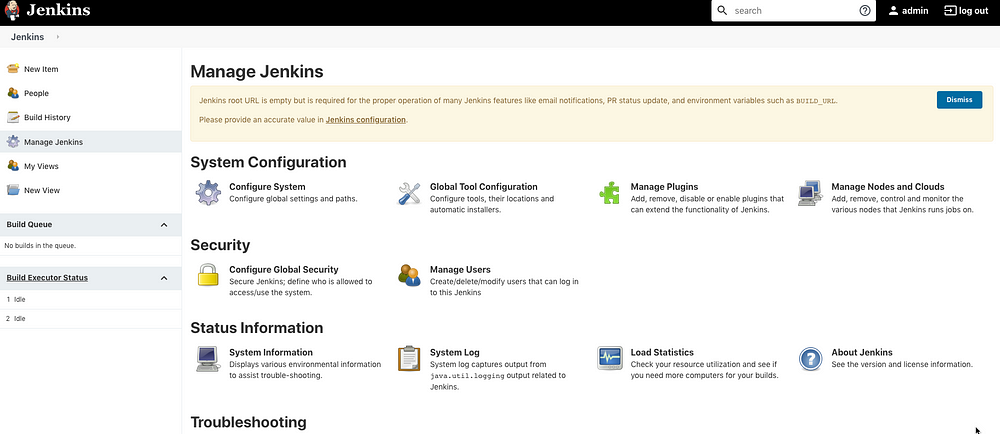
Perfect, we are in
# Next step, install plugins and create first admin account
# Ref



 Khoá học lập trình game con rắn cho trẻ em
Khoá học lập trình game con rắn cho trẻ em 


