What is this article about ?
What is HAProxy ?
Install HAProxy
Configure the load balancer
Use HAProxy to balance Websocket traffic
Use HAProxy to configue backup server
HAProxy algo
Use HAProxy to Observe all requests for errors
Use HAProxy to Monitor for server downtime
Use HAProxy to send logs to syslog
Separating errors into their own log file
Redirecting HTTP traffic to HTTPS
URL rewriting
Security: basic Auth
Security :Denying requests from an attacker for a time
Security: whitelist IP Address
What is HAProxy ?
In simple, HAProxy is a free, very fast and reliable solution offering high availability, load balancing, and proxying for TCP and HTTP-based applications. It is particularly suited for very high traffic web sites and powers quite a number of the world’s most visited ones.
Install HAProxy
Issue the command below to install haproxy:
sudo yum install haproxy
Enable it and start it
sudo systemctl restart haproxy
sudo systemctl enable haproxy
Configure the load balancer
The HAProxy basic configuration file is located at
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
An HAProxy basic configuration informs the load balancing system on what kind of connections it should be listening for and which servers it should relay the connections to.
We are going to create a configuration file /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg containing the necessary settings and configurations.
sudo nano /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Enter the following into the file:
global log /dev/log local0 log /dev/log local1 notice chroot /var/lib/haproxy stats socket /run/haproxy/admin.sock mode 660 level admin stats timeout 30s user haproxy group haproxy daemon defaults log global mode http option httplog option dontlognull timeout connect 5000 timeout client 50000 timeout server 50000 frontend http_front bind *:80 stats uri /haproxy?stats default_backend http_back backend http_back balance roundrobin server my_server private_IP:80 check server my_server private_IP:80 check
Ensure to save the file before closing it.
Next, restart Haproxy using the command below:
sudo systemctl restart haproxy
sudo systemctl enable haproxy
Use HAProxy to balance Websocket traffic
Websocket is where HAProxy take advantage of nginx and apache.
Take a look at at, and You can use this configuration below:
global log 127.0.0.1 local0 maxconn 8192 user haproxy group haproxy defaults log global mode http option httplog option http-server-close option dontlognull option redispatch option contstats retries 3 backlog 10000 timeout client 35s timeout connect 5s timeout server 35s timeout tunnel 3600s timeout http-keep-alive 1s timeout http-request 15s timeout queue 30s timeout tarpit 60s default-server inter 3s rise 2 fall 3 option forwardfor listen stats bind *:8080 stats enable stats hide-version stats realm Haproxy\ Statistics stats uri /status stats auth user:password frontend public bind *:80 maxconn 10000 acl is_websocket hdr_end(host) -i ws.node-example.com use_backend ws if is_websocket default_backend www backend www timeout check 5000 option httpchk GET /status?haproxy=1 balance roundrobin server www1 10.142.0.3:3001 maxconn 1000 weight 10 cookie websrv_www check inter 10000 rise 1 fall 3 server www2 10.142.0.6:3001 maxconn 1000 weight 10 cookie websrv_www check inter 10000 rise 1 fall 3 backend ws timeout check 5000 option httpchk GET /status?haproxy=1 balance roundrobin cookie HAPROXY_COOKIE insert indirect nocache server ws1 10.142.0.4:3002 maxconn 1000 weight 10 cookie websrv_ws check inter 10000 rise 1 fall 3 check cookie ws1 server ws2 10.142.0.7:3002 maxconn 1000 weight 10 cookie websrv_ws check inter 10000 rise 1 fall 3 check cookie ws2
Use HAProxy to configue backup server
Now, if both service1 and service2 go offline, we will try to let service3 and service4 take over. The config is below:
backend webservice balance roundrobin server service1 192.168.50.10:80 check server service2 192.168.50.11:80 check server service3 192.168.50.12:80 check backup server service4 192.168.50.13:80 check backup option allbackups
HAProxy algo
The roundrobin algorithm
The weighted roundrobin algorithm
The leastconn algorithm
The weighted leastconn algorithm
The hash uri algorithm
The first available algorithm
Use HAProxy to Observe all requests for errors
In the following example, we monitor all connections to the db1 server for errors. If we see three
consecutive failed connections, we will take the server offline just like we would if we’d had three
failed health checks.
backend msql_databases mode tcp balance roundrobin server db1 192.168.50.20:3306 check fall 3 inter 2m observe layer4 error-limit 1 server db2 192.168.50.21:3306 check backup
or
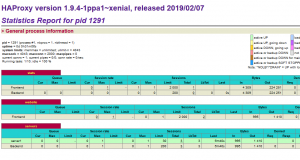
Use HAProxy to Monitor for server downtime
It is quite simple
defaults stats enable
And you can have a look at stats
Use HAProxy to send logs to syslog
HAProxy comes ready to use syslog. The HAProxy executable calls syslog functions, which are
written into its source code, whenever it encounters something noteworthy. These function calls create
the log messages. In our /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg file, we need to specify where to send this data. By
default, Ubuntu has a socket listening at /dev/log that we can send syslog events to. Update the /etc/
haproxy/haproxy.cfg file’s global section so that it contains a log directive that points to this socket.
Config
global log /dev/log local0 info
The first parameter tells HAProxy where syslog is listening. For the second parameter, we pass
local0 as the facility, which identifies the program doing the logging. There are a number of
predefined facilities, such as cron, mail and kern, but since there isn’t a built-in facility for haproxy, we
use one of the generic, any-purpose local designations. We can use the local0 through local7 facilities.
The third parameter sets the events, by level of importance, that we’d like to log. The levels, from most
to least important, are: emerg, alert, crit, err, warning, notice, info and debug
Separating errors into their own log file
Add option log-separate-errors
You can look at the sample config
log global option log-separate-errors
More notes:
From most important to least, they are: emerg,
alert, crit, err, warning, notice, info and debug
Redirecting HTTP traffic to HTTPS
The sample config is below
frontend mywebsite
bind *:80
bind *:443 ssl crt /etc/ssl/certs/mywebsite_cert.pem
redirect scheme https if !{ ssl_fc }
default_backend webservers
backend webservers
balance roundrobin
server web1 192.168.50.12:80 check
server web2 192.168.50.13:80 check
URL rewriting
Security : basic auth
Now, we try to Configure Basic authentication by adding a new section called userlist to the /etc/haproxy/
haproxy.cfg file.
In the following example, we define a list of usernames and passwords in a
userlist section that I’ve decided to call TrustedPeople:
Sample config
userlist TrustedPeople user bob insecure-password password123 user alice insecure-password anotherpassword
Security : Denying requests from an attacker for a time
When we detect that a user may be abusing our website, we can deny their requests for a certain
amount of time. We’ll build on the example where we tracked each client’s connection rate. In the
following snippet, when a client’s connection rate is too high, we flag them as an abuser and deny their
requests for two minutes.
Example config below
frontend mywebsite bind *:80 default_backend webservers stick-table type ip size 200k expire 2m store conn_rate(3s),gpc0 acl conn_rate_abuse sc0_conn_rate gt 60 acl flag_as_abuser sc0_inc_gpc0 gt 0 acl is_abuser src_get_gpc0 gt 0 http-request track-sc0 src http-request deny if is_abuser http-request deny if conn_rate_abuse flag_as_abuser
Security : Whitelisting IP addresses
Sometimes, you may want to allow a set of IP addresses that are whitelisted to always be accepted,
even if they trigger rules that would have otherwise denied them. In the following example, we store
the client’s error rate in a stick-table by using the http_err_rate data type. If, over a
sampled time of five seconds, the client receives more than 10 errors, such as HTTP 404 Not Found,
then we flag them as an abuser and deny them until the record in the table expires. We’ve set the
expiration time to two minutes.
Sample config
frontend mywebsite bind *:80 stick-table type ip size 200k expire 2m store http_err_rate(5s),gpc0 acl too_many_errors src_http_err_rate gt 10 acl flag_as_abuser sc0_inc_gpc0 gt 0 acl is_abuser src_get_gpc0 gt 0 acl whitelisted src 10.0.0.0/8 172.16.0.0/12 192.168.0.0/16 http-request track-sc0 src http-request allow if whitelisted http-request deny if is_abuser http-request deny if too_many_errors flag_as_abuser default_backend webservers
# Ref
http://www.haproxy.org/
https://cloudwafer.com/blog/installing-haproxy-on-centos-7/
https://gist.github.com/Philmod/21b7c8fbd5a2bc20987141bc99966951



 Khoá học lập trình game con rắn cho trẻ em
Khoá học lập trình game con rắn cho trẻ em 


